Remote control technology & 14a EnWG: Making EV charging infrastructure grid-compatible

Whether courier, fleet or in-house logistics: More and more companies are electrifying their vehicle fleets. But with the shift to e-mobility comes increased grid load. Operators of multiple charge points need solutions that power their fleets efficiently while also supporting grid stability. This is where remote control technology comes into play and with it, the question: How can charging infrastructure be integrated into the power grid so that grid operators can intervene without disrupting operations?
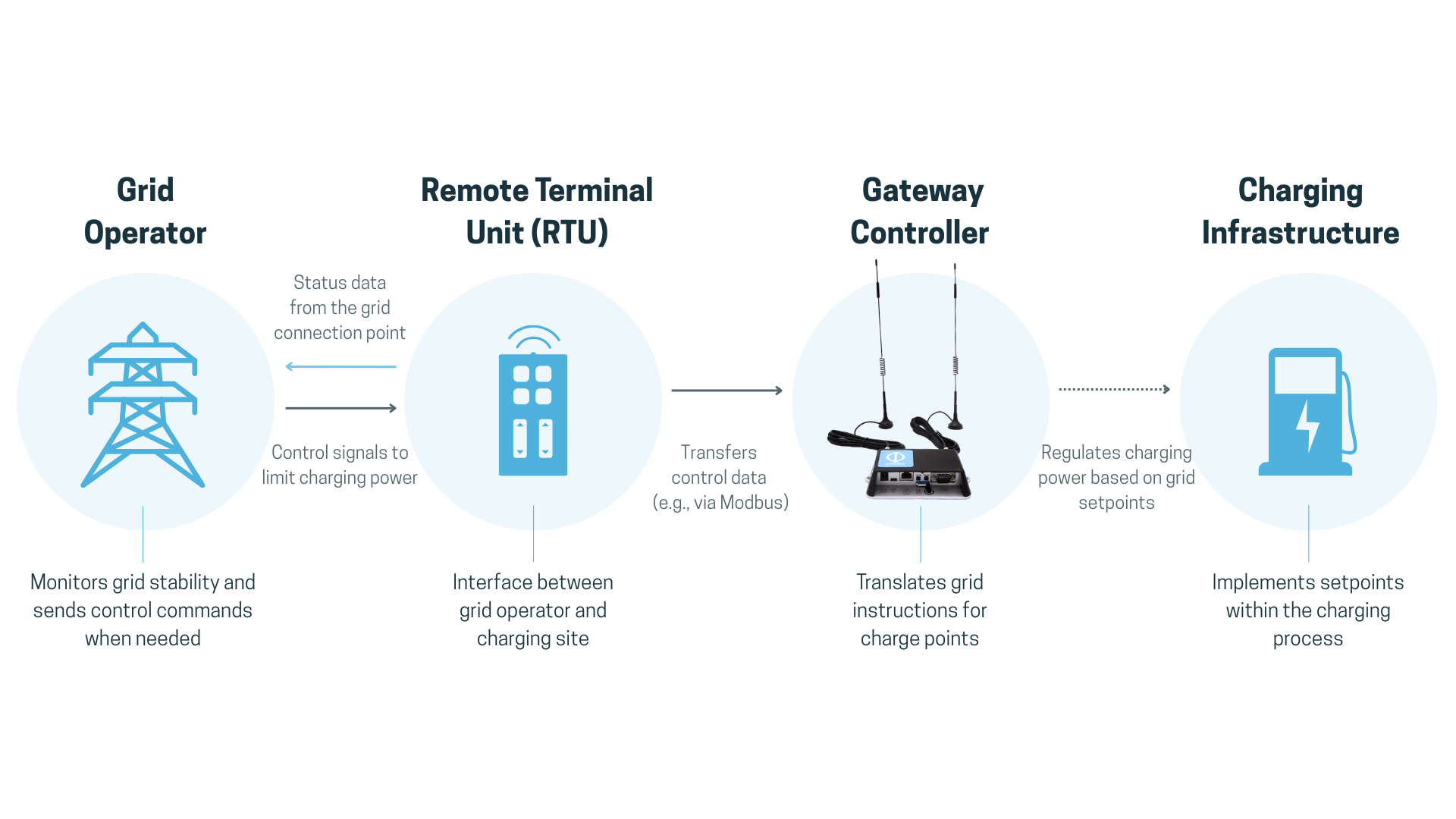
Remote control technology enables technical systems to be monitored and controlled via communication interfaces. In the context of electromobility, this means grid operators do not access the infrastructure directly but send setpoints – such as a cap on maximum active power that the charging infrastructure implements automatically. The goal: prevent grid overload and maintain power grid stability.
–
As the number of electric vehicles increases, so does pressure on local grids – especially in large logistics depots. To maintain grid stability, operators must be able to throttle or control high-demand systems like charging points. This requirement is legally anchored in Section 14a of the German Energy Industry Act (EnWG). It defines charging infrastructure as a controllable consumption device – allowing grid operators to influence consumption during peak loads.
To enable this, the infrastructure must support remote control capabilities. Our smart charging software fulfills this requirement, aligning with both regulatory and grid-specific standards to ensure compatibility and control.
Remote control technology allows grid operators to interact with charging infrastructure – particularly in critical load situations. Here’s how the process typically unfolds:
For this process to function smoothly, a clearly defined interface is essential, including a data point list from the grid operator specifying the information to be exchanged (e.g., setpoint/actual values, time stamps).
This document defines the exact communication between the RTU and the grid operator. Each grid provider may specify its own requirements. Typically, these include:
Our smart charging software is able to read and interpret these parameters and translate them into precise commands to the charge points – automated, regulation-compliant and in real time.
| Model | Communication | Advantages | Limitations | Typical Use Case |
| Potential-free contacts | Binary (on/off) | Simple, robust, cost-effective | No fine-grained control | Smaller/older grid zones |
| Modbus TCP | Serial (RTU) or IP-based (TCP) | Common, standardized, flexible | Limited security features (TCP variant) | Widely used for charging hardware, well supported |
| IEC 60870-5-101 | Serial (e.g., RS-232/485) | Secure, grid-proven, real-time capable | Complex implementation, often mandated by grid side | Large power systems, some charging depots |
IEC 60870-5-104 | TCP/IP-based grid protocol | Advanced control options, well integrated | Higher integration effort, detailed configuration | Grid SCADA systems, direct grid operator connections |
| OpenADR (Automated Demand Response) | Internet-based demand-response protocol | Flexible, future-proof for smart energy systems | Rare in EU; limited adoption | Rare in EU; limited adoptionEher in USA oder bei innovativen Demand-Response-Projekten |
Rolling out remote control capabilities is rarely straightforward, mainly due to multiple stakeholders:
This is where our smart charging software becomes a key enabler. It bridges technical gaps between stakeholders, ensures protocol compatibility, and streamlines project execution—from initial interface analysis to real-time data exchange. Our experience helps identify common pitfalls and implement proven solutions.
In collaboration with TST Group, grid operator EWR, transformer specialist Mprotec, and charging hardware provider GP JOULE CONNECT, a successful remote control integration was implemented. Mprotec installed the RTU at the grid transfer point. Communication occurs via a Modbus-based data point list.
EWR sends setpoints to limit the active power – e.g., 70% of the maximum available load. Our software receives and interprets this input via the defined Modbus interface and dynamically adjusts the charging schedule accordingly.
This ensures that – despite load restrictions – the charging process remains efficient and vehicle availability is maintained. No manual intervention needed.
In daily operation, this means stable, grid-compliant charging, even when grid operators actively control the load. For logistics, it’s a crucial factor in maintaining reliable fleet operations.
Implementing remote control technology projects typically requires tailored technical coordination and a certain degree of engineering – especially when dealing with complex grid requirements or larger charging sites. Our intelligent charging solution is highly adaptable and supports all common remote control protocols, such as Modbus TCP or IEC 60870-5-10X.
We provide end-to-end support – from parameter configuration and data point mapping to coordinated test runs and final commissioning. This ensures that every project is grid-compliant and perfectly aligned with your specific requirements.
Large-scale charging infrastructure – especially in logistics –requires seamless grid integration. Remote control technology makes that possible. But without adaptable software, even the best hardware remains underutilized.
Our platform helps logistics operators run stable, grid-aligned charging systems. It ensures communication with grid stakeholders, automates control commands, and integrates with operational needs. What sounds abstract on paper becomes a working system – with tangible benefits for your electric fleet.
Book a consultation to learn how our software enables seamless integration of remote control into your fleet charging operations.
Questions about the product?
Send an email to
Technical questions?Send an email to
Support-Tel.:
+49 461 402 142-10